Commmand Line Tool
SeisFlows is primarily interacted with via command line calls and a
parameter file. In this page we explain how to use this command line
tool to create a SeisFlows parameters file, edit and configure it, and
establish a SeisFlows working directory. We also provide explanation for
other command line options which act as helper utilities for improved
package control.
After installing SeisFlows into a Conda environment, the seisflows
command will be available directly from the command line. To access the
help dialogue, you can type seisflows or seisflows -h
seisflows
usage: seisflows [-h] [-w [WORKDIR]] [-p [PARAMETER_FILE]]
{setup,configure,swap,init,submit,resume,restart,clean,par,sempar,check,print,reset,debug,examples}
...
================================================================================
SeisFlows: Waveform Inversion Package
================================================================================
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-w [WORKDIR], --workdir [WORKDIR]
The SeisFlows working directory, default: cwd
-p [PARAMETER_FILE], --parameter_file [PARAMETER_FILE]
Parameters file, default: 'parameters.yaml'
command:
Available SeisFlows arguments and their intended usages
setup Setup working directory from scratch
configure Fill parameter file with defaults
swap Swap module parameters in an existing parameter file
init Initiate working environment
submit Submit initial workflow to system
resume Re-submit previous workflow to system
restart Remove current environment and submit new workflow
clean Remove files relating to an active working environment
par View and edit SeisFlows parameter file
sempar View and edit SPECFEM parameter file
check Check state of an active environment
print Print information related to an active environment
reset Reset modules within an active state
debug Start interactive debug environment
examples Look at and run pre-configured example problems
'seisflows [command] -h' for more detailed descriptions of each command.
Setting up
seisflows setup
The first step of any SeisFlows workflow is to setting up a parameter
file. The seisflows setup command copies in a template parameter
file.
cd ~/Scratch
rm *
ls
/Users/Chow/Scratch
seisflows setup -h
usage: seisflows setup [-h] [-f]
In the specified working directory, copy template parameter file containing
only module choices, and symlink source code for both the base and super
repositories for easy edit access. If a parameter file matching the provided
name exists in the working directory, a prompt will appear asking the user if
they want to overwrite.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f, --force automatically overwrites existing parameter file
# The '-f' flag (overwrite) will overwrite any existing parameter file
seisflows setup -f
creating parameter file: parameters.yaml
Having a look at the template parameters.yaml file that was just
generated, we can see that it contains some pre-defined default values
for the core SeisFlows modules. Each of these modules defines it’s own
set of unique parameters which make up a workflow.
ls
wc -l parameters.yaml # List the number of lines in the file
parameters.yaml sflog.txt
30 parameters.yaml
cat parameters.yaml
# //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#
# SeisFlows YAML Parameter File
#
# //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#
# Modules correspond to the structure of the source code, and determine
# SeisFlows' behavior at runtime. Each module requires its own sub-parameters.
#
# .. rubric::
# - To determine available options for modules listed below, run:
# > seisflows print modules
# - To auto-fill with docstrings and default values (recommended), run:
# > seisflows configure
# - To set values as NoneType, use: null
# - To set values as infinity, use: inf
#
# MODULES
# ///////
# workflow (str): The types and order of functions for running SeisFlows
# system (str): Computer architecture of the system being used
# solver (str): External numerical solver to use for waveform simulations
# preprocess (str): Preprocessing schema for waveform data
# optimize (str): Optimization algorithm for the inverse problem
# ==============================================================================
workflow: forward
system: workstation
solver: specfem2d
preprocess: default
optimize: gradient
seisflows configure
We can now run the seisflows configure command which will build out
our parameter file based on the module choices provided in the parameter
file.
seisflows configure -h
usage: seisflows configure [-h] [-a]
SeisFlows parameter files will vary depending on chosen modules and their
respective required parameters. This function will dynamically traverse the
source code and generate a template parameter file based on module choices.
The resulting file incldues docstrings and type hints for each parameter.
Optional parameters will be set with default values and required parameters
and paths will be marked appropriately. Required parameters must be set before
a workflow can be submitted.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-a, --absolute_paths Set default paths relative to cwd
seisflows configure
head -200 parameters.yaml | tail -n 82 # have a look at the middle of the file
echo
wc -l parameters.yaml
# :param smooth_v: Gaussian half-width for vertical smoothing in units
# of meters.
# :type components: str
# :param components: components to consider and tag data with. Should be
# string of letters such as 'RTZ'
# :type solver_io: str
# :param solver_io: format of model/kernel/gradient files expected by the
# numerical solver. Available: ['fortran_binary': default .bin files].
# TODO: ['adios': ADIOS formatted files]
# :type source_prefix: str
# :param source_prefix: prefix of source/event/earthquake files. If None,
# will attempt to guess based on the specific solver chosen.
# :type mpiexec: str
# :param mpiexec: MPI executable used to run parallel processes. Should also
# be defined for the system module
#
#
# Solver SPECFEM2D
# ----------------
# SPECFEM2D-specific alterations to the base SPECFEM module
#
# Parameters
# ----------
# :type source_prefix: str
# :param source_prefix: Prefix of source files in path SPECFEM_DATA. Defaults
# to 'SOURCE'
# :type multiples: bool
# :param multiples: set an absorbing top-boundary condition
#
#
# =============================================================================
syn_data_format: ascii
materials: acoustic
density: False
attenuation: False
smooth_h: 0.0
smooth_v: 0.0
components: ZNE
source_prefix: SOURCE
multiples: False
# =============================================================================
#
# Default Preprocess
# ------------------
# Data processing for seismic traces, with options for data misfit,
# filtering, normalization and muting.
#
# Parameters
# ----------
# :type syn_data_format: str
# :param syn_data_format: data format for reading synthetic traces into
# memory. Shared with solver module. For available see:
# seisflows.plugins.preprocess.readers
# :type obs_data_format: str
# :param obs_data_format: data format for reading observed traces into
# memory. For available see: seisflows.plugins.preprocess.readers
# :type misfit: str
# :param misfit: misfit function for waveform comparisons. For available
# see seisflows.plugins.preprocess.misfit
# :type backproject: str
# :param backproject: backprojection function for migration, or the
# objective function in FWI. For available see
# seisflows.plugins.preprocess.adjoint
# :type normalize: str
# :param normalize: Data normalization parameters used to normalize the
# amplitudes of waveforms. Choose from two sets:
# ENORML1: normalize per event by L1 of traces; OR
# ENORML2: normalize per event by L2 of traces;
# &
# TNORML1: normalize per trace by L1 of itself; OR
# TNORML2: normalize per trace by L2 of itself
# :type filter: str
# :param filter: Data filtering type, available options are:
# BANDPASS (req. MIN/MAX PERIOD/FREQ);
# LOWPASS (req. MAX_FREQ or MIN_PERIOD);
# HIGHPASS (req. MIN_FREQ or MAX_PERIOD)
# :type min_period: float
# :param min_period: Minimum filter period applied to time series.
# See also MIN_FREQ, MAX_FREQ, if User defines FREQ parameters, they
# will overwrite PERIOD parameters.
# :type max_period: float
# :param max_period: Maximum filter period applied to time series. See
# also MIN_FREQ, MAX_FREQ, if User defines FREQ parameters, they will
# overwrite PERIOD parameters.
# :type min_freq: float
# :param min_freq: Maximum filter frequency applied to time series,
337 parameters.yaml
We can see that our parameter file is over 300 lines, a bit too cumbersome to print on the page. The length of the file mostly arises from the header, as each parameter gets it’s own entry with the parameter’s type, docstring, and any available options. Each set of parameters are separated by their relevant module, and their respective docstrings should help users understand how and when they are used in a SeisFlows workflow.
NOTE: Many parameters have sensible default values chosen, but it is up to the user to decide which parameters are relevant to them, and how they would like them set. Internal check functions throughout the package will raise AssertionErrors for incorrectly or improperly set parameters.
Editing the parameter file
seisflows par
You can always open your favorite text editor to make changes to the
parameter file, however the seisflows par command makes things
easier by allowing you to view and edit values from the command line.
This makes it convenient to change parameters quickly and allows you to
script your parameter file setup for improved reproducibility.
seisflows par -h
usage: seisflows par [-h] [-p] [parameter] [value]
Directly edit values in the parameter file by providing the parameter and
corresponding value. If no value is provided, will simply print out the
current value of the given parameter. Works also with path names.
positional arguments:
parameter Parameter to edit or view, (case independent).
value Optional value to set parameter to. If not given, will
print out current parameter. If given, will replace
current parameter with new value. Set as 'null' for
NoneType and set '' for empty string
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p, --skip_print Skip the print statement which is typically sent to stdout
after changing parameters.
The call structure of the par command is provided in the help
message:
seisflows par [parameter] [value (optional)]
We can view parameters by providing a single ‘parameter’ argument to the
par command
seisflows par ntask # ntask is the number of tasks/events to be run during a workflow
ntask: 1
We can change a given parameter from it’s original value by providing a second ‘value’ argument
seisflows par ntask 3
ntask: 1 -> 3
seisflows sempar
The seisflows sempar command behaves the same as the par
command, except is used to edit a SPECFEM2D/3D/3D_GLOBE Par_file. It has
the same call structure as par.
seisflows check
Each module contains it’s own internal set of parameter checks which
make sure that reasonable parameter values and types have been chosen.
This is especially important when submitting large jobs on clusters as
the check function will allow the User to catch errors without
having to wait on queue times or waste computational resources.
seisflows check
================================================================================
PARAMETER ERRROR
////////////////
path_specfem_bin must exist and must point to directory containing SPECFEM
executables
================================================================================
Here we can see that a given path has not been set correctly in the parameter file.
seisflows swap
The seisflows swap command allows you to swap out a set of module
parameters without affecting other parts of the parameter file. Some
cases for when this might be useful include switching from a
‘workstation’ system to a ‘cluster’ system, or swapping solvers from
‘specfem2d’ to ‘specfem3d’.
seisflows swap -h
usage: seisflows swap [-h] [module] [classname]
During workflow development, it may be necessary to swap between different
sub-modules (e.g., system.workstation -> system.cluster). However this would
typically involving re-generating and re-filling a parameter file. The 'swap'
function makes it easier to swap parameters between modules.
positional arguments:
module Module name to swap
classname Classname to swap to
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Running workflows
seisflows submit
To run SeisFlows, we use the submit call. This will submit the
workflow to the system and continue until a User-defined stop
criteria is met.
Under the hood, the submit function will differ depending on the
chosen system. For Users running on laptops and workstations,
submit will simply launch a Python process and step through the
tasks in the workflow task list. On clusters, submit will launch
a master job on a compute node, which will itself step through tasks in
the task list, ensuring that no processing is run on login nodes.
seisflows submit -h
usage: seisflows submit [-h] [-s STOP_AFTER]
The main SeisFlows execution command. Submit a SeisFlows workflow to the
chosen system, equal to executing seisflows.workflow.main(). This function
will create and fill the working directory with required paths, perform path
and parameter error checking, and establish the active working environment
before executing the workflow.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s STOP_AFTER, --stop_after STOP_AFTER
Optional override of the 'STOP_AFTER' parameter
seisflows clean
The clean function is used to clear an existing working directory.
It deletes all SeisFlows created files and directories using paths in
the parameter file, but does not delete the parameter file itself. Use
the -f/--force flag to skip over the ‘are you sure?’ check
statement.
seisflows clean -h
usage: seisflows clean [-h] [-f]
Delete all SeisFlows related files in the working directory, except for the
parameter file.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f, --force Skip the warning check that precedes the clean function
seisflows restart
The restart function is a convenience function which wraps clean
and submit. It is used to restart workflows using the same parameter
file. It also takes the -f/--force flag that the clean function
defines.
seisflows restart -h
usage: seisflows restart [-h] [-f]
Akin to running seisflows clean; seisflows submit. Restarts the workflow by
removing the current state and submitting a fresh workflow.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f, --force Skip the clean warning check statement
Plotting
from IPython.display import Image # Required for showing inline figures in notebook/docs
seisflows plot2d
plot2d allows you to quickly plot SPECFEM2D models, kernels and
gradients which have been exported to disk during a SeisFlows workflow.
From a SeisFlows working directory the format for running plot2d is
provided in the help message.
# a directory where we have run an example problem
cd ~/sfexamples/example_2
ls
/home/bchow/Work/work/seisflows_example/example_2
logs parameters.yaml sflog.txt specfem2d
output scratch sfstate.txt specfem2d_workdir
seisflows plot2d -h
usage: seisflows plot2d [-h] [-c [CMAP]] [-s [SAVEFIG]] [name] [parameter]
Plots model/kernels/gradient files located in the output/
directory. ONLY available for SPECFEM2D models.
positional arguments:
name Name of directory in the output/ directory
parameter Name of parameter to plot from name. E.g., 'vs',
'vp' etc.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c [CMAP], --cmap [CMAP]
colormap to be passed to PyPlot
-s [SAVEFIG], --savefig [SAVEFIG]
optional name and path to save figure
Running plot2d without any arguments will print out a list of
available directories you can plot
seisflows plot2d
PLOT2D
//////
Available models/gradients/kernels
GRADIENT_01
GRADIENT_02
MODEL_01
MODEL_02
MODEL_INIT
MODEL_TRUE
Users will also have to choose which parameter they would like to plot, which is defined by the available parameters in the underlying model. Incorrect choices will throw an AssertionError which will tell you what parameters are available to plot.
seisflows plot2d GRADIENT_01
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/bchow/miniconda3/envs/docs/bin/seisflows", line 33, in <module>
sys.exit(load_entry_point('seisflows', 'console_scripts', 'seisflows')())
File "/home/bchow/REPOSITORIES/seisflows/seisflows/seisflows.py", line 1383, in main
sf()
File "/home/bchow/REPOSITORIES/seisflows/seisflows/seisflows.py", line 438, in __call__
getattr(self, self._args.command)(**vars(self._args))
File "/home/bchow/REPOSITORIES/seisflows/seisflows/seisflows.py", line 1106, in plot2d
save=savefig)
File "/home/bchow/REPOSITORIES/seisflows/seisflows/tools/specfem.py", line 428, in plot2d
f"chosen parameter must be in {self._parameters}"
AssertionError: chosen parameter must be in ['vp_kernel', 'vs_kernel']
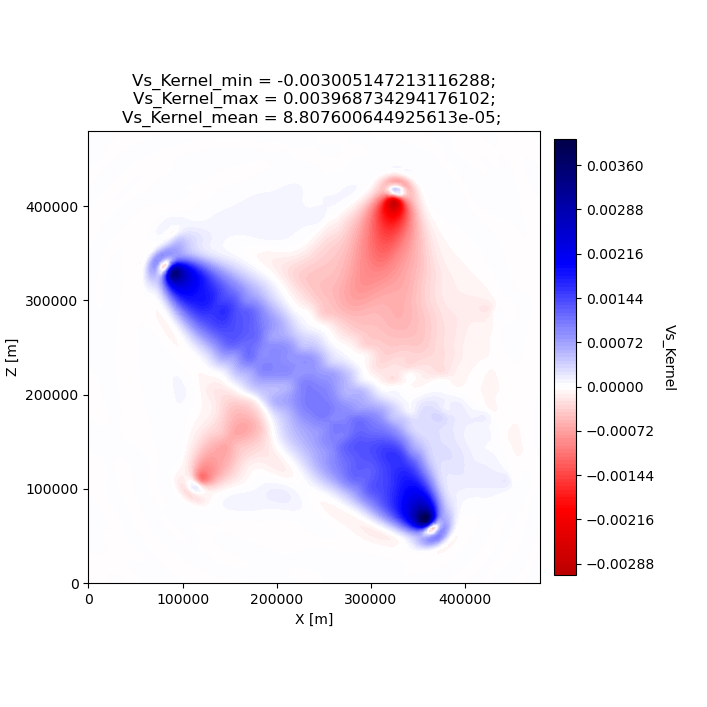
seisflows plot2d GRADIENT_01 vs_kernel --savefig gradient_01_vs_kernel.png
Image(filename='gradient_01_vs_kernel.png')
Figure(707.107x707.107)
seisflows plotst
plotst (i.e., plot stream) is a wrapper for ObsPy’s
Stream.plot() which plots waveforms generated by the external numerical
solver. In this case we have generated waveforms in the ASCII format
during one of our example problems. Using the export_traces
parameter, our workflow has saved these waveforms to the output/
directory of our SeisFlows working directory.
cd ~/sfexamples/example_3/output/solver/001/syn
ls
/home/bchow/Work/work/seisflows_example/example_3/output/solver/001/syn
AA.S000000.BXY.semd AA.S000009.BXY.semd AA.S000018.BXY.semd
AA.S000001.BXY.semd AA.S000010.BXY.semd AA.S000019.BXY.semd
AA.S000002.BXY.semd AA.S000011.BXY.semd AA.S000020.BXY.semd
AA.S000003.BXY.semd AA.S000012.BXY.semd AA.S000021.BXY.semd
AA.S000004.BXY.semd AA.S000013.BXY.semd AA.S000022.BXY.semd
AA.S000005.BXY.semd AA.S000014.BXY.semd AA.S000023.BXY.semd
AA.S000006.BXY.semd AA.S000015.BXY.semd AA.S000024.BXY.semd
AA.S000007.BXY.semd AA.S000016.BXY.semd
AA.S000008.BXY.semd AA.S000017.BXY.semd
# Run the help message
seisflows plotst -h
usage: seisflows plotst [-h] [--data_format [DATA_FORMAT]] [-s [SAVEFIG]]
[fids [fids ...]]
Plots waveforms output by the solver. Uses ObsPy's
Stream.plot() function under the hood. Example call would be
seisflows plotst scratch/solver/mainsolver/traces/syn/*
positional arguments:
fids File IDs to be passed to plotting. Wildcards
acceptable
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--data_format [DATA_FORMAT]
Data format of the files. Must match file type that
SeisFlows can read. These include:['SU', 'ASCII',
'SAC']. Defaults to 'ASCII'. See
SeisFlows.preprocess.default.read() for all options.
-s [SAVEFIG], --savefig [SAVEFIG]
optional name and path to save figure
# Plot a single synthetic seismogram
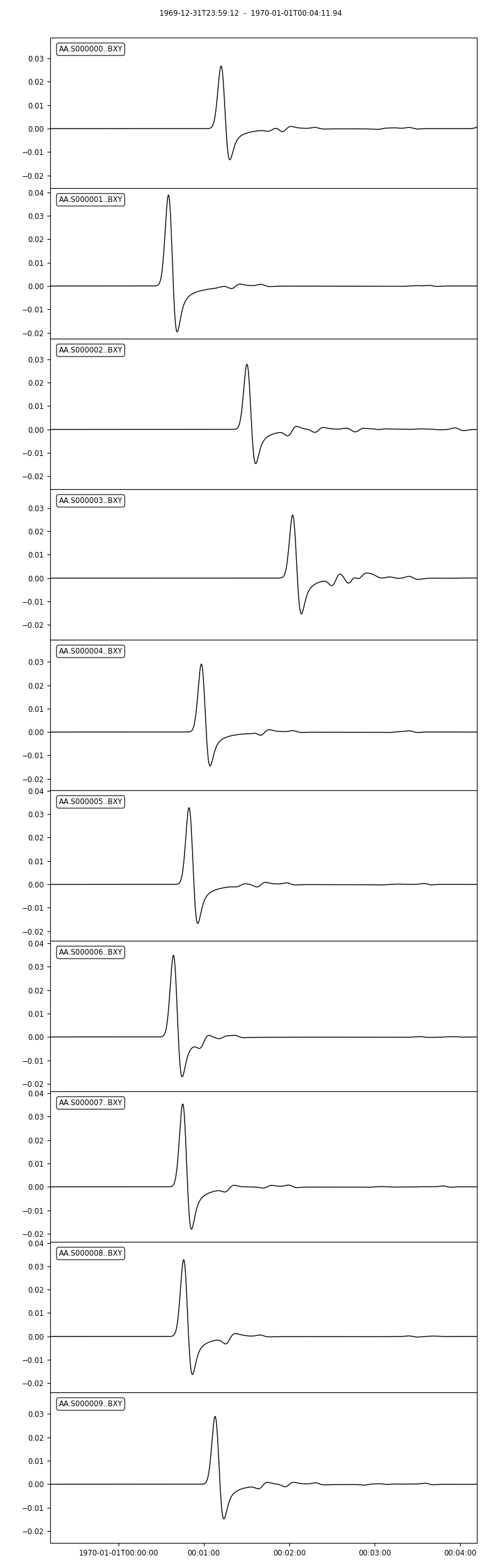
seisflows plotst AA.S000000.BXY.semd --savefig AA.S000000.BXY.semd.png
Image("AA.S000000.BXY.semd.png")
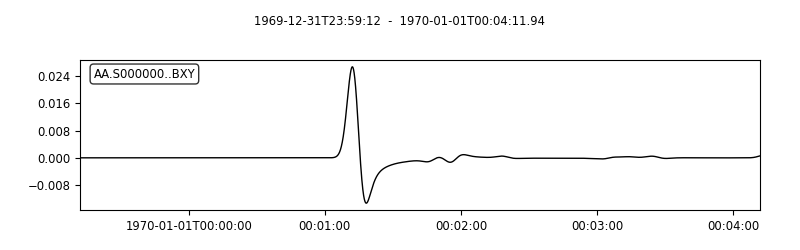
# Use wild cards to plot multiple stations at once
seisflows plotst AA.S00000?.BXY.semd --savefig AA.S00000X.BXY.semd.png
Image("AA.S00000X.BXY.semd.png")